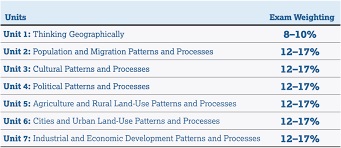
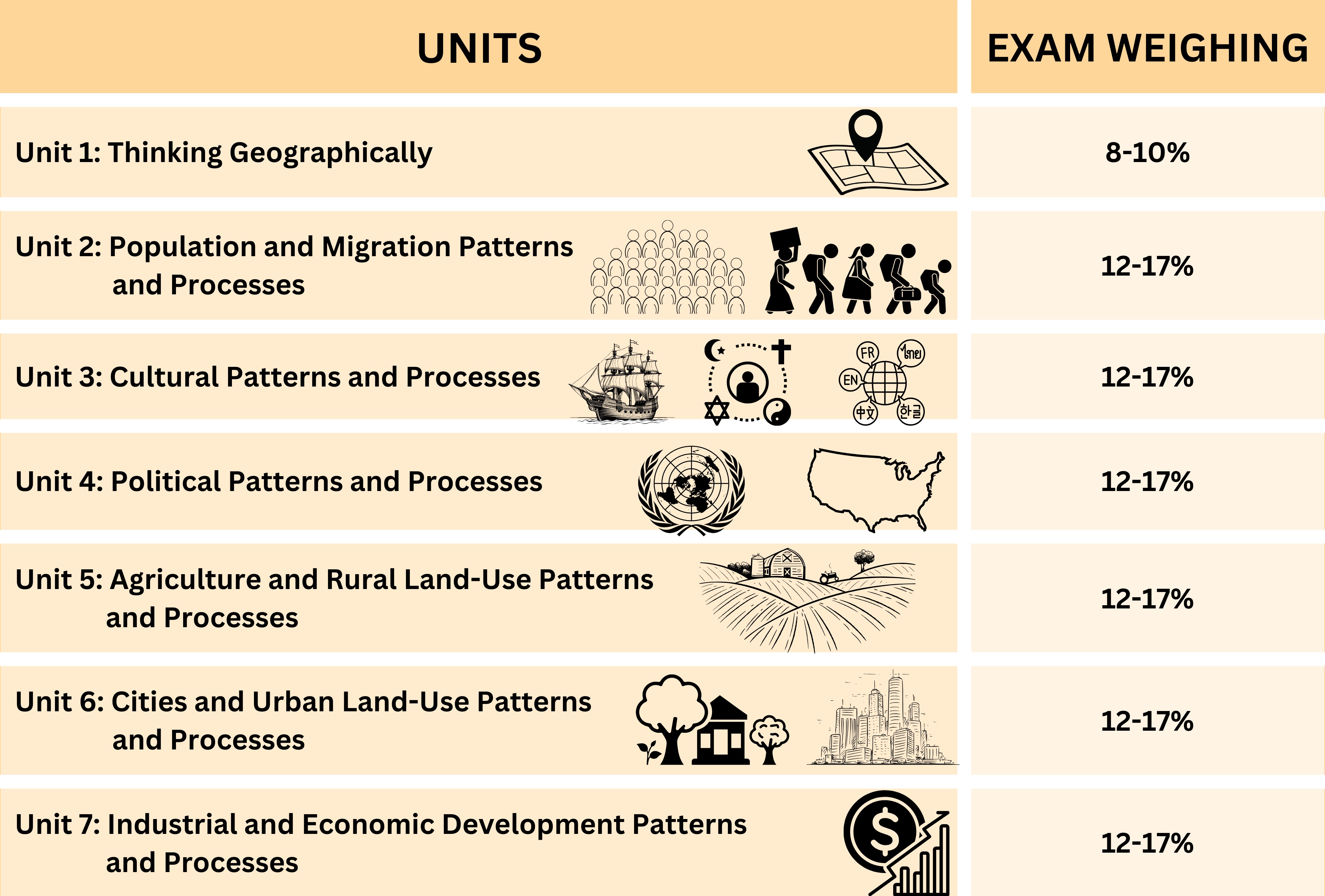
Unit 1: Geography: Its Nature and Perspectives
- Key Topics:
- The study of geography: Physical vs. Human Geography
- Geographic tools: Maps, GIS (Geographic Information Systems), and remote sensing
- Spatial analysis: How and why things are located where they are
- The importance of scale, space, and place
- Types of maps (e.g., choropleth, cartograms, topographic)
- Human-environment interaction and sustainability
- Learning Objectives:
- Understand basic geographic concepts and vocabulary
- Apply geographic tools to analyze spatial patterns
- Investigate the relationship between geography and human activities
Unit 2: Population and Migration
- Key Topics:
- Population distribution and density
- Demographic transition model (DTM)
- Population pyramids and their implications
- Factors influencing migration (economic, political, environmental)
- Push and pull factors in migration
- Refugees, asylum seekers, and global migration trends
- Learning Objectives:
- Analyze population trends and their impact on society
- Understand migration theories and patterns
- Examine the social, economic, and political consequences of migration
Unit 3: Cultural Patterns and Processes
- Key Topics:
- The concept of culture: language, religion, ethnicity, and cultural landscapes
- Cultural diffusion and globalization
- Language families and distribution
- The spread of religions and belief systems
- Ethnicities and cultural identities
- Impact of cultural interactions on geography
- Learning Objectives:
- Recognize cultural landscapes and understand their meaning
- Analyze the spread of cultural traits across regions
- Examine the role of cultural diversity in human geography
Unit 4: Political Geography
- Key Topics:
- States, nations, and nation-states
- Boundaries and borders: Political divisions and their challenges
- Geopolitics: The relationship between geography and political power
- Electoral geography and voting patterns
- Supranational organizations (e.g., UN, EU, NATO)
- Conflicts, territorial disputes, and the impact of globalization on politics
- Learning Objectives:
- Understand the concepts of states, sovereignty, and territoriality
- Explore the impact of geography on political systems and governance
- Analyze global conflicts and territorial disputes
Unit 5: Agriculture and Rural Land Use
- Key Topics:
- Agricultural revolutions and their impact on society
- Types of agriculture: Subsistence vs. commercial
- Theories of agricultural land use (e.g., von Thünen model)
- The Green Revolution and its environmental consequences
- Rural land use and settlement patterns
- The role of agriculture in the global economy
- Learning Objectives:
- Understand the relationship between agriculture and geography
- Analyze the impact of agricultural practices on rural communities and economies
- Examine global agricultural challenges and innovations
Unit 6: Industrialization and Economic Development
- Key Topics:
- The Industrial Revolution and its global effects
- Economic sectors: Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary
- Models of economic development (e.g., Rostow’s Stages of Growth)
- Global economic networks and trade routes
- The impact of globalization on economic development
- Economic disparities and development issues
- Learning Objectives:
- Identify and understand the key drivers of economic development
- Examine the global distribution of industries and economic activities
- Analyze the consequences of global trade and industrialization
Unit 7: Cities and Urban Land Use
- Key Topics:
- The development of cities: Urbanization and suburbanization
- Theories of urban models (e.g., Burgess's Concentric Zone Model, Hoyt’s Sector Model)
- Urban sprawl and sustainable city planning
- Global cities and urban networks
- Challenges of urbanization: Housing, transportation, pollution, and inequality
- Learning Objectives:
- Analyze the spatial organization of cities and their growth patterns
- Investigate the environmental, social, and economic challenges of urbanization
- Understand the principles of sustainable urban planning and development
Unit 8: Environment and Sustainability
- Key Topics:
- Human-environment interaction and sustainability
- Environmental challenges: Climate change, deforestation, desertification
- Environmental management and conservation efforts
- The role of geography in addressing global environmental issues
- Sustainable development and the impact of global policies
- Learning Objectives:
- Understand the relationship between human activities and environmental change
- Analyze the causes and effects of environmental problems
- Evaluate global strategies for sustainability and conservation
Unit 9: Globalization and Its Impacts
- Key Topics:
- Theories of globalization and its economic, political, and cultural dimensions
- The impact of multinational corporations and international trade
- The role of technology in globalization
- Cultural homogenization vs. cultural diversity
- The challenges and opportunities of global interconnectedness
- Learning Objectives:
- Examine the causes and effects of globalization in different regions
- Analyze the role of international organizations in global governance
- Understand the tension between global integration and local cultures
Assessment Overview:
- Formative Assessments: Quizzes, discussions, map analyses, and small group activities to gauge understanding of key concepts.
- Summative Assessments: Periodic tests, research projects, and essays to assess mastery of the course material.
- AP Exam: The course culminates in the AP Human Geography exam, which consists of multiple-choice questions and free-response questions designed to test students’ knowledge and analytical skills.
- This course outline covers the broad and diverse topics we’ll study throughout the year. Each unit builds on the next, helping you understand how geography plays a crucial role in shaping our world. Let’s dive in and explore the fascinating connections between people, places, and the environment!
|