| Home Page | Web Dev Students | AP Comp Students | Coach B Site | Student Grades |
 |
| PINE MOUNTAIN CLUB WEATHER |
Latest Pine Mountain Club Community Photo

--Online Distance Learning Assignments and Information--
Download AP Computer Science Syllabus
AP Test Information
Section I: End-of-Course Multiple-Choice Exam- Thursday May 14, 2026 at 12pm in the WR Gym.
70 Multiple-Choice Questions | 120 Minutes | 70% of Score | 4 answer options
57 single-select multiple-choice
5 single-select with reading passage about a computing innovation
8 multiple-select multiple-choice: select 2 answers
Section II: Create Performance Task- Project Due Tuesday April 30, 8:59pm PST.
30% of Score
Students will develop a computer program of their choice. Students need at least 16 hours of in-class time to complete.
Written Response questions about Your Code on AP Exam Day.
AP Computer Science Principles Period Information
Period 1 |
Period 3 |
Period 5 |
Code.org Class Code- |
Code.org Class Code- |
Code.org Class Code- |
AP Test Class Code- XDM32L |
AP Test Class Code- QJJXWY |
AP Test Class Code- G9X2MA |
2025-2026 2nd Semester Assignments, Help, and Information
View 1st Semester Daily Project, Vocab, and Lessons
Week 8 |
||
Day 17- Monday March 2- Unit 7 (24-25)- Lessons 1-3 Parameters and Return (6pts) All work from last Thursday due at start of class today! Lessons 2 & 3 due at end of class today- 6pts Lesson 1- Parameters and Return Explore- 0pts
Lesson 2- Parameters and Return Investigate- 3pts In this lesson, students work with friends to investigate two different apps that use parameters and return values.
Lesson 3- Parameters and Return Practice- 3pts Students practice writing programs with parameters and return values by creating and debugging functions that use them
Feel Free to Start on Lesson 4- Parameters and Return Make You will have Wednesday to complete Lesson 4.
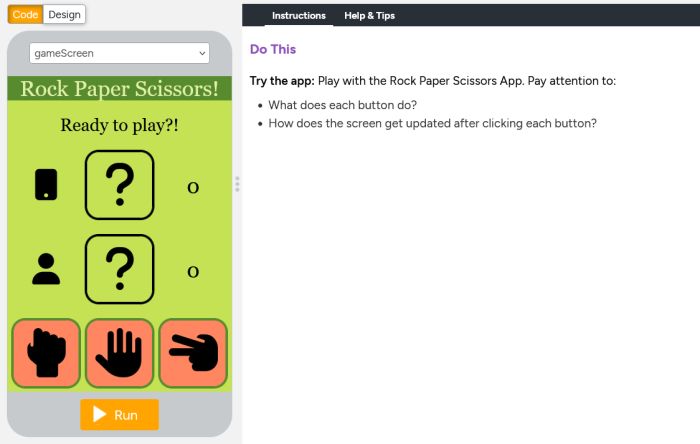
Day 18- Wednesday March 4- Unit 7 (24-25)- Lesson 4 Student Wellness Survey- Per 1 During WRTV Using Programming Patterns and a step-by-step approach students make their own version of a Reminder app. At the beginning of the lesson students are able to explore a working version of the app. They are then given the design elements of the app but begin with a blank screen. Students use an Activity Guide to go through the high level steps they should use to develop their app but leaves it to them to decide how to write the code. At the end students submit their apps and answer a free-response question in the style of a Create performance task written response prompt. Student apps and written responses can be assessed using a provided rubric. Complete Lesson 4- Rock, Paper, Scissors App- 10pts Parameters and Return Make Rock, Paper, Scissors Activity Guide- 5pts, 1-3 Students Help Video for App and Activity Guide Lesson 4 Completion and Activity Guide Due at End of Class today- 15pts Total
Day 19- Friday March 6- Unit 7 (24-25)- Lessons 5-7 Libraries- 9pts Lesson 5- Libraries Explore- 3pts Students learn the basics of libraries while building upon the envelope model of a function with a folder to represent a library.
Lesson 6- Libraries Investigate- 3pts In this lesson students work with partners to investigate two apps that use libraries as well as the code used to make a library. Through a series of guided discussions they learn how libraries help programmers simplify and reuse their code.
Lesson 7- Libraries Practice- 3pts Students practice important skills for working with libraries, including testing and debugging libraries, and using libraries to help develop apps. After a brief introduction to these practices by the teacher, students spend the majority of their time programming in a level progression. When we program with libraries we can use functions that take care of difficult or repetitive tasks. Instead of focusing on these details we can focus on the big picture of what it is that we want our programs to do and just assume that those details are handled by library functions. As we'll see in today's lesson that leads to two important realizations.
|
Week 7 |
||
Day 15- Tuesday February 24- Unit 6 (24-25)- Lesson 13- Hackathon Project Unit 6 Quiz- 15pts Hackathon PAirs Project
Day 16- Thursday February 26- Unit 6 (24-25)- Finish Hackathon Project Finish the Hackathon Project. Lesson 13
|
Week 6 |
||
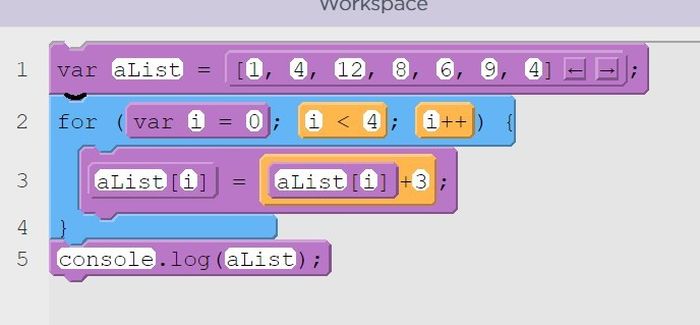
Day 13- Wednesday February 18- Unit 6 (24-25)- Traversals Leesons 9-11 I am absent today. My wife, Max, and I are digging out from all of the snow we got in Pine Mountain Club. Please take GREAT care of my sub! I will be back at school on Friday for sure! Lesson 9 Explore- 3pts The lesson begins with a quick review of lists and loops before moving into the main activity. Here students explore the concept with the Traversal Machine, a physical model of traversal using a for loop.
Lesson 10 Investigate- 3pts In this lesson students work with partners to investigate three different apps that use traversals to access items in a lists. Students first explore all three apps without seeing the code to notice similarities and predict how they will work. Then they explore the code itself and make additions and modifications to the apps. To conclude the lesson, students review and discuss common programming patterns with traversals.
Lesson 11 Practice- 3pts
Students practice traversing lists, filtering and reducing lists, and using the data import tools. Along the way students develop debugging practices with traversals.
Lessons 9-11 Due at End of Class Today! 9pts
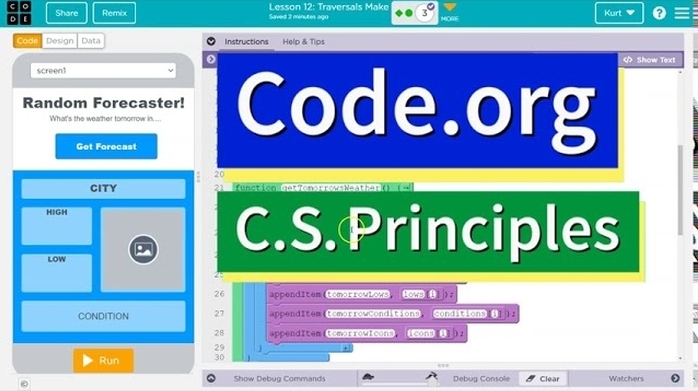
Day 14- Friday February 20- Unit 6 (24-25)- Lesson 12- Traversals Make Lesson 12- Traversals Make Using Programming Patterns and a step-by-step approach students make their own version of a Random Forecaster app. At the beginning of the lesson students are able to explore a working version of the app. They are then given the design elements of the app but begin with a blank screen. Students use an Activity Guide to go through the high level steps they should use to develop their app but leaves it to them to decide how to write the code. At the end students submit their apps and answer a free-response question in the style of a Create performance task written response prompt. Student apps and written responses can be assessed using a provided rubric.
Next Week-
|
Week 5 |
||
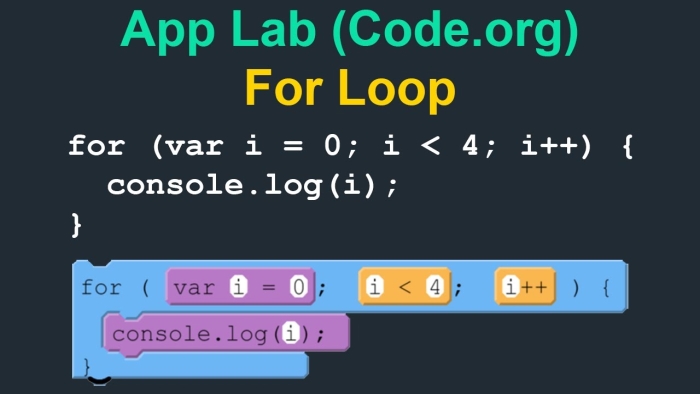
Day 11- Tuesday February 10- Unit 6 (24-25)- Loops Lessons 5-7 9 Points, 2 Points for Each Lesson Lesson 5- Loops Explore Students are introduced to the concept of loops.
Lesson 6- Loops Investigate Students practice using the for loop in order to repeatedly run pieces of code. The lesson begins with a quick investigation of an app that flips coins. After that code investigation students complete another investigation with an app that uses loops to update screen elements.
Lesson 7- Loops Practice Students practice the basics of loops including using while loops, for loops, and updating multiple screen elements with a for loop. Along the way students develop debugging practices with loops.
All 3 Lessons Due at the End of the Class Today
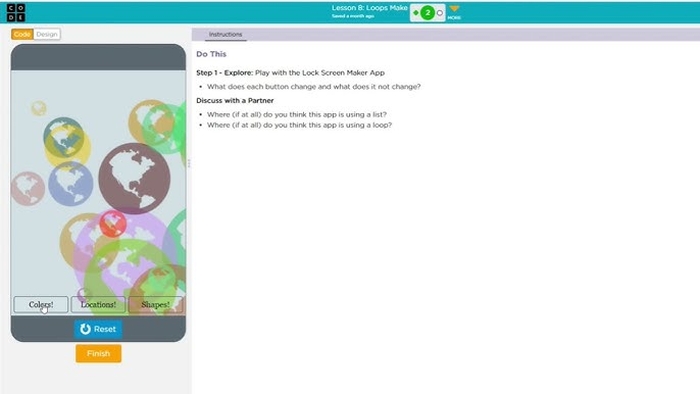
Day 12- Thursday February 12- Unit 6 (24-25)- Lesson 8- Loops Make Using Programming Patterns and a step-by-step approach students make their own version of a Lock Screen Maker app. At the beginning of the lesson students are able to explore a working version of the app. They are then given the design elements of the app but begin with minimal starting code. A progression of levels guides students on the high level steps they should use to develop their app but leaves it to them to decide how to write the code. At the end students submit their apps and answer a free-response question in the style of a Create performance task written response prompt. Student apps and written responses can be assessed using a provided rubric. Lesson 8- Loops Make
App, Lesson 8, and Activity Guide Due at end of Class Today! Traversals Next Week
|
Week 4 |
||
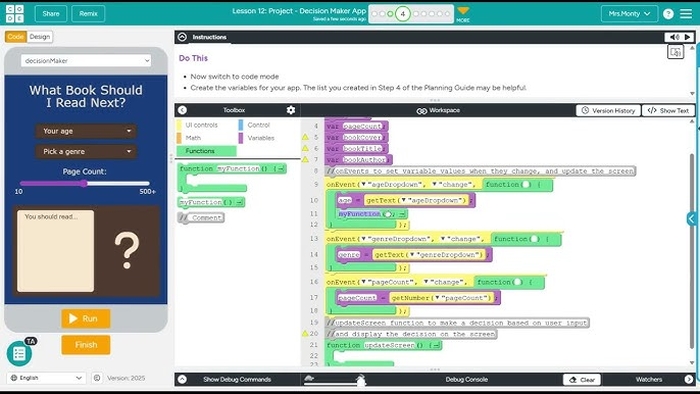
Day 8- Monday February 2- Unit 4 (24-25)- Lesson 12- Finish Decision Maker App
I am with my dad in the hospital today, nothing too serious. But he needs a family member with him. So I got dad tomorrow. Thanks for your support and understanding! See you Wednesday with all your work done! Take great care of my sub!!
Finish Decision Maker App- 15pts Lesson 12- Decision Maker App Project- 30pts Total Using a Project Planning Guide, students work through the stages of creating an app from scratch.
All Items for the Decision Maker App Project is due at start of class on Wednesday February 4.
Day 9- Wednesday February 4- Unit 6 (24-25)- Lists Explore, Investigate, and Practice
// All Decision Maker App Items Due at Start of Class Today! // // Thanks for being great for my sub on Monday! //
--Lists, Loops, and Traversals Unit-- This unit introduces lists, loops, and traversals, and explores the way they can be used to build apps that store and process large amounts of information. Learn to program with the data library in App Lab and complete a hackathon project at the end of the unit where you can design a program about any topic of your choosing.
Lesson 1- Lists Explore Introduce the syntax to use lists and the ways they can be used.
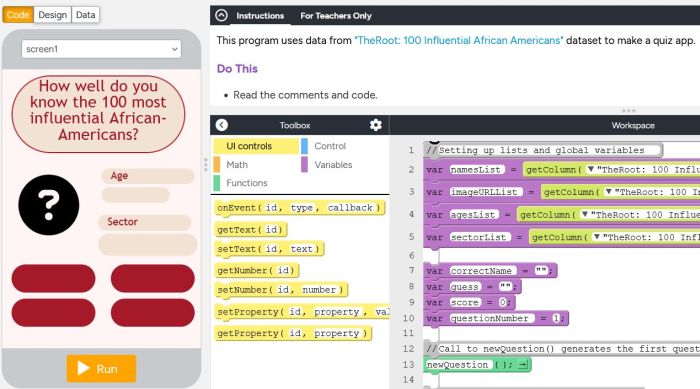
Lesson 2- Lists Investigate In this lesson students work with others to investigate three different apps that use lists. Students first explore all three apps without seeing the code to notice similarities and predict how they will work. Then they explore the code itself and make additions and modifications to the apps. Students are also introduced to the getColumn command and how to use it to populate lists from the datasets in the AppLab Data Library.
Lesson 2- Lists Practice Practice the basics of lists including creating lists and accessing, inserting, and removing elements from lists.
Lessons 1-3 Due by end of class today! 9pts Total
Day 10- Friday February 6- Unit 6 (24-25)- Lesson 4- Lists Make Activity Guide, Checklist, Rubric, and Performance Task Practice Question- 5pts, (1-3 Students) Complete Lesson 4- Lists Make- 10pts Using Programming Patterns and a step-by-step approach students make their own version of a Reminder app. At the beginning of the lesson students are able to explore a working version of the app. They are then given the design elements of the app but begin with a blank screen. Students use an Activity Guide to go through the high level steps they should use to develop their app but leaves it to them to decide how to write the code. At the end students submit their apps and answer a free-response question in the style of a Create performance task written response prompt. Activity Guide and Lesson 4 Completion Due at End of Class Today- 15pts Total
|
Week 3 |
||
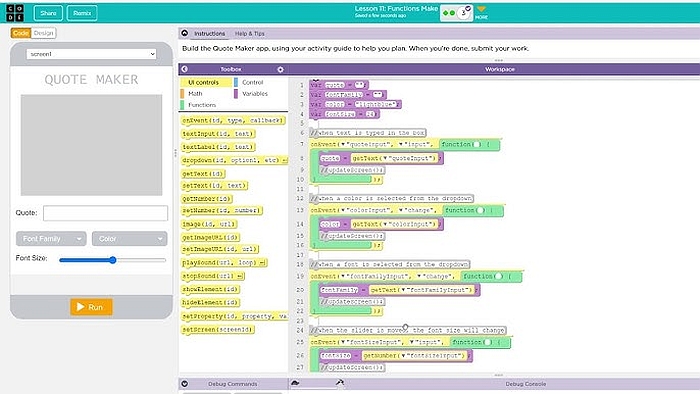
Day 6- Tuesday January 27- Unit 4 (24-25)- Lesson 11- Functions Make Using Programming Patterns and a step-by-step approach students make their own version of a Quote Maker app. At the beginning of the lesson students are able to explore a working version of the app. They are then given the design elements of the app but begin with a blank screen. Students use an Activity Guide to go through the high level steps they should use to develop their app but leaves it to them to decide how to write the code. At the end students submit their apps and answer a free-response question in the style of a Create performance task written response prompt. Student apps and written responses can be assessed using a provided rubric. Lesson 11- Functions Make
Day 7- Thursday January 29- Unit 4 (24-25)- Lesson 12- Decision Maker App Multiple Choice Quiz- 15 Questions, 15 Points- Variables, Conditionals, and Functions Decision Maker App- 15pts Lesson 12- Decision Maker App Project- 30pts Total Using a Project Planning Guide, students work through the stages of creating an app from scratch.
All Items for the Decision Maker App Project is due at start of class on Wednesday February 4.
|
Week 2 |
||
Day 4- Wednesdaay January 21- Unit 4 (24-25)- Conditionals Lesson 8 Using Programming Patterns and a step-by-step approach students make their own version of a Museum Ticket Generator app. At the beginning of the lesson students are able to explore a working version of the app. They are then given the design elements of the app but begin with a blank screen. A progression of levels guides students on the high level steps they should use to develop their app but leaves it to them to decide how to write the code. At the end students submit their apps and answer a free-response question in the style of a Create performance task written response prompt.
Day 5- Friday January 23- Unit 4 (24-25)- Functions Lessons 9 & 10 Coach B Help Slides for Functions Lessons 9 & 10 Lesson 9- Functions Explore/Investigate
Lesson 10- Functions Practice
Lessons 9 & 10 Due at end of class- 5pts
====== Coming Next Week ====== You can get started on following tasks if you want... Tuesday- Lesson 11- Functions Make
Thursday- Lesson 12- Project
|
Week 1 |
||
Day 1- Monday January 12- Unit 4 (24-25)- Variables Lessons 1-3 Welcome back! Hope you all had a great winter break. I missed almost all of you!! Let's get into some higher level programming... let's roll. ** NEW SEATING CHART DAY **Unit 4 Information-
Lesson 1- Variables Explore
Lesson 2- Variables Investigate
Lesson 3- Variables Practice
Finish Lessons 1-3- 5pts
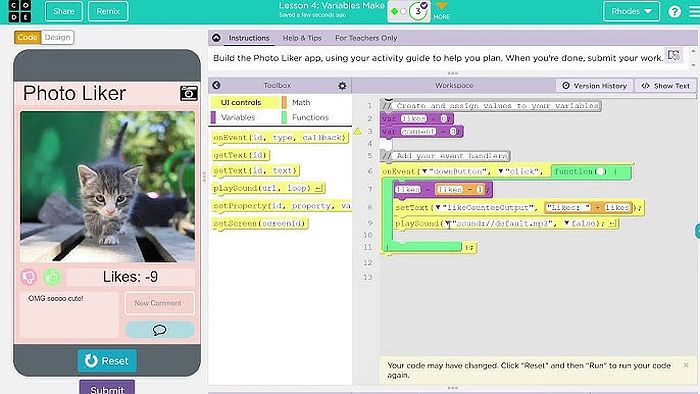
Day 2- Wednesday January 14- Lesson 4- Variables Make Lesson 4- Variables Make Using Programming Patterns and a step-by-step approach students make their own version of a Photo Liker app. At the beginning of the lesson students are able to explore a working version of the app. They are then given the design elements of the app but begin with a blank screen. A progression of levels guides students on the high level steps they should use to develop their app but leaves it to them to decide how to write the code. At the end students submit their apps and answer a free-response question in the style of a Create performance task written response prompt. Student apps and written responses can be assessed using a provided rubric.
Day 3- Friday January 16- Unit 4 (24-25)- Conditionals Lessons 5-7 Lesson 5- Conditionals Explore
Lesson 6- Conditionals Investigate
Lesson 7- Conditionals Practice
Finish Lessons 5-7- 5pts ============================== Wednesday Next Week-
|